Lymphoma Confusion? Key Differences & Similarities Explained!
Are you struggling to understand the complexities of lymphoma and its various forms? The world of health can feel overwhelming, but understanding the differences between Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma is crucial for anyone seeking clarity.
When it comes to understanding your health, certain terms can feel overwhelming, especially when they sound so similar. Both are types of lymphomaa cancer that begins in your lymphatic systembut their differences go far beyond just their names. These conditions are both lymphomas, which means that they are cancers involving lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell (WBC)but they differ in their microscopic appearances, typical disease course, and other characteristics. Playing a key role in the bodys immune function, lymphocytes help fight off infections. Both share similarities, such as the involvement of lymph nodes. Both can affect adults and children, and symptoms for both include swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, fatigue and weight loss. However, they typically develop in different areas of the body and have different symptoms and outlooks. Although both diseases can be diagnosed at any age, Hodgkin lymphoma is most common in young adults ages 15 to 40 and older adults over age 55. This article seeks to compare and contrast the two diseases, showing the characteristics of each, including the significant similarities and the key differences between them.
Let's delve deeper into these two conditions to provide a clearer understanding.
To illustrate further, imagine our well-being, its resilience can be impacted by various factors.
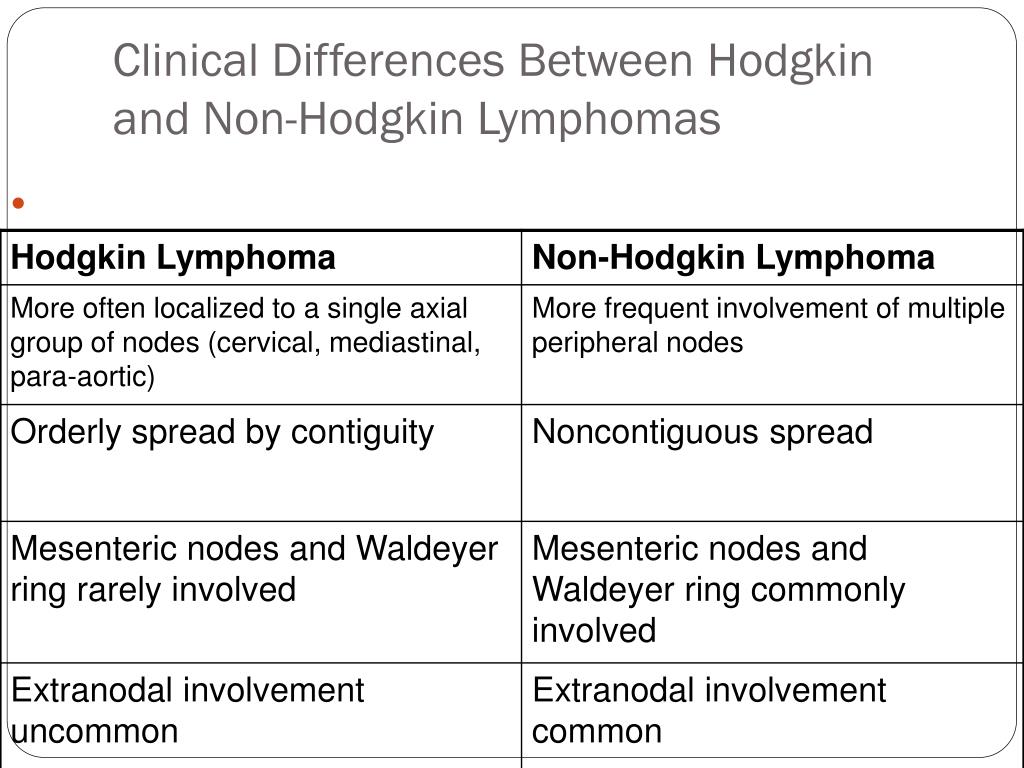
Understanding the Differences
These two diseases may sound similar, but these cancers have distinct differences. There are two general categories of the different types of lymphoma. Both originate in a type of white blood cell in your immune system known as a lymphocyte. Lymphocytes help your immune system remain strong by protecting your body from germs. However, there are key differences between them.
Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL)
Hodgkin lymphoma has a distinctive characteristic: the presence of a specific type of abnormal cell known as the Reed-Sternberg cell. This abnormal cell is a large, mutant lymphocyte. The origin and behavior of these cells are central to the diagnosis and treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma. There are only two main forms of Hodgkin lymphoma: Classic (more than 90 percent of all cases) and nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. Often considered more treatable with a higher cure rate. Hodgkin's lymphoma is considered potentially curable. Survival after treatment for lymphoma varies a lot from cancer to cancer and person to person. For information on Hodgkin lymphoma click here.
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) encompasses a much broader range of lymphomas, each with its own unique characteristics. It accounts for approximately 90% of all lymphoma cases and has an unpredictable nature due to its varied subtypes. This page will provide an overview of NHL.
The landscape of lymphoma is diverse, and recognizing these differences is essential for effective diagnosis and management. Some viruses may make you.
In a complex world of medical terminology, understanding the nuances between Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma is vital for patients, families, and anyone seeking to deepen their knowledge of health. By focusing on the distinct characteristics of each type, we empower individuals with the knowledge needed to navigate this challenging disease landscape.
Here's a breakdown to further clarify the key differences and similarities, providing a comprehensive view of both Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma:
As always, eye-opening information.
Similarities
- Both are cancers of the lymphatic system.
- Both involve lymphocytes.
- Both can cause swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, fatigue, and weight loss.
- Both can affect both adults and children.
Differences
- Hodgkin lymphoma is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, while non-Hodgkin lymphoma does not have this specific cell.
- Hodgkin lymphoma has two main forms, while non-Hodgkin lymphoma has a wide variety of subtypes.
- The treatment and prognosis can vary significantly between the two types, and also within the subtypes of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, a type of large, abnormal lymphocyte. These cells are the hallmark of the disease. Hodgkin's lymphoma occurs only in young adults b. It has a bimodal age distribution, meaning it tends to affect young adults (15-40 years old) and older adults (over 55). Classic Hodgkin lymphoma is the most common type, accounting for the majority of cases. Hodgkin lymphoma is often considered more treatable and potentially curable, particularly when diagnosed at an early stage.
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a vast category encompassing a wide range of lymphoma subtypes. It does not have Reed-Sternberg cells. It is far more common than Hodgkin lymphoma. The subtypes of NHL vary greatly, each with different characteristics, treatments, and prognoses. The subtypes are categorized based on the type of lymphocyte affected (B-cell or T-cell) and the aggressiveness of the cancer (indolent or aggressive). Because of the variety of subtypes, treatment and prognosis vary widely.
Survival after treatment for lymphoma varies a lot from cancer to cancer and person to person.
The information presented here is for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
The key to addressing these conditions lies in early detection and personalized treatment plans.
The information is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of these two distinct types of lymphoma.